Child Not Speaking?
An INDO-AMERICAN Child Development Centre with 26+ Years of Experience in Speech Therapy & Occupational Therapy.
We have seen the tremendous improvement in children after utilizing LITERATURE & EVIDENCE BASED THERAPY TECHNIQUES… and that is our strength.




About Us
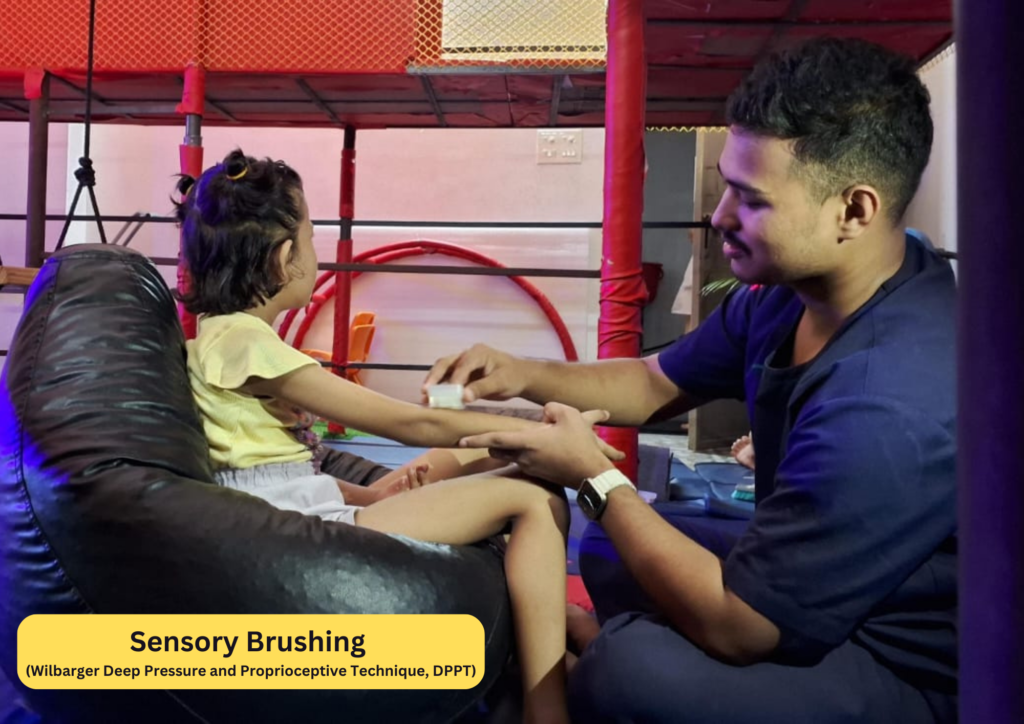
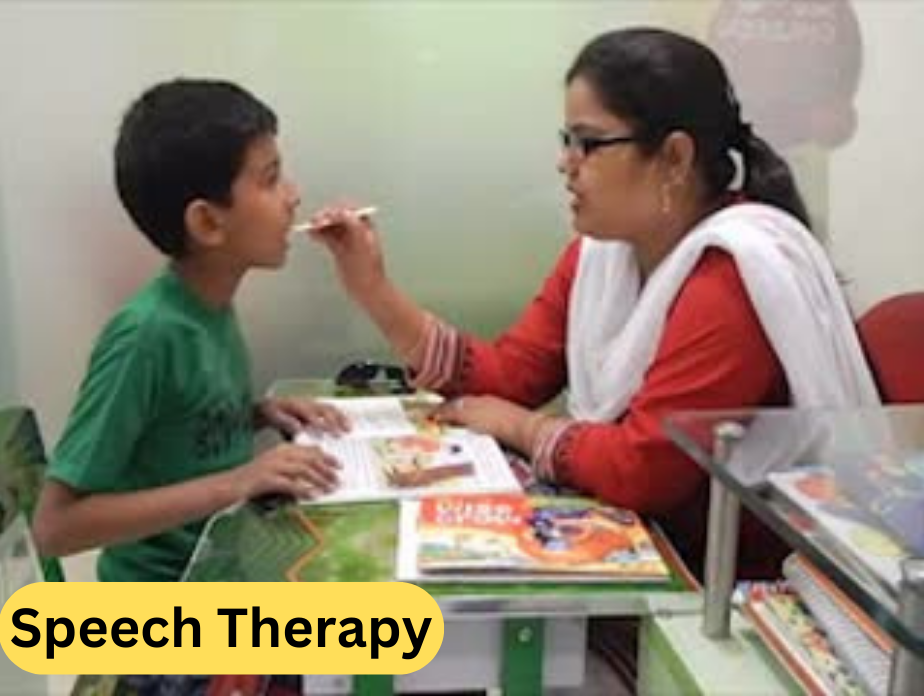
We are in the child development sector since last 3 decades. Our only strength is accurate diagnosis and research based therapy approach. This evidence based therapy approach helped our children to develop rapidly. Cooper is a pioneer in Speech Therapy, Occupational Therapy, Special Education, Autism and other childhood developmental difficulties.
Our Services
Why Cooper Child Development Centre
Evidence Based Therapy Approaches
Rapid Improvement
Parent training for Home Practice
Affordable
We provide Therapy Services for:
- Developmental Delay (DD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD)
- Global Developmental Delay (GDD)
- Late Language Emergence
- Learning Disability (Dyslexia, Dysgraphia)
- Specific Language Impairment (SLI)
- Cleft Lip and Palate
- Down's Syndrom
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Phonological Disorder
- Pragmatic Language Disorder
- Apraxia of Speech
- Aphonia or Dysphonia
- Normal Nonfluency
- Fluency Disoder (Stuttering/Cluttering)
- Misarticulation
- Seizure Disorder
- Sensory Processing Disorder
- Spina Bifida
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Dementia
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Cochlear Implant
- Hearing Loss (Using Hearing Aid)
- Aphasia
- Dysarthria
- Motor Speech Disorder
- Neurological Language Disorder
- Other Developmental Difficulties...
Conditions We Treat
What Our Happy Parents Say...
We were blank, literally can't explain. Doctor recommended Speech Therapy and Occupational Therapy. We started immediately there but we are basically from Sikkim hence it was not possible to stay there for long so we started searching for a good centre in Siliguri. Visited Many Centres but finally met Dr. Tania ma'am, owner of the centre I think, she is rally very knowledgeble and updated about Children with Autism.
We are taking therapy here since last 6 months and my daughter is in sentence level. We don't want anything else ma'am, I can't explain our emotion ma'am for your support.
Thank you very very much ma'am. This feedback is just a small contribution from us to Cooper. God bless you all always.
My nephew (Pratyush) who is diagnosed with Autism and was doing therapy for last 1 and half year. There was no much improvement. I found Cooper Child Development Centre and visited here. Doing Therapy here since last 4 months. When we came here, we got to know that Pratyush has no Autism et al. There are definitely some signs but presenting some signs doesn't mean a child has Autism. Thanks to the doctor.
The therapy process became completely different here and we can see drastic change in 4 months as compare to last 1 and half years. Thank you guys, you people are doing great work and after all a best Social work.
Lets Don't Waste The Critical Age of the Child
Almost 90% of the child’s brain development completed in the early developmental period (Critical Age Hypothesis), after that age, the ability to learn things gets harder as it goes.


FAQ
Autism in children refers to Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) as it manifests during early development. It typically becomes apparent in the first few years of life, though the signs can vary widely. Here are some key features:
Social Challenges: Children with autism may struggle with understanding social cues, making eye contact, or engaging in typical play with peers. They might have difficulty expressing their feelings or understanding others’ emotions.
Communication Difficulties: This can include delayed speech development, difficulty initiating conversations, or challenges in understanding language nuances. Some children may be non-verbal, while others may have advanced language skills but struggle with social use of language.
Repetitive Behaviors: Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements (like rocking or hand-flapping), insist on sameness in routines, or develop intense interests in specific topics.
Sensory Sensitivities: Children on the spectrum may have heightened or reduced sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures, leading to discomfort or fascination.
Variability in Skills: Autism is a spectrum, so some children may have intellectual disabilities, while others may have average or above-average intelligence and excel in specific areas.
Common signs and symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can vary widely, but they generally fall into two main categories: social communication challenges and repetitive behaviors. Here are some specific indicators:
Social Communication Challenges
Difficulty with Social Interactions:
- Limited eye contact or facial expressions.
- Difficulty understanding or responding to social cues.
- Challenges in initiating or maintaining conversations.
Struggles with Non-Verbal Communication:
- Limited use of gestures (e.g., waving, pointing).
- Difficulty interpreting body language or tone of voice.
Delayed Speech and Language Skills:
- Limited verbal communication or not speaking at all.
- Echolalia (repeating phrases or sentences without understanding).
Challenges in Sharing Interests:
- Difficulty engaging in pretend play or sharing enjoyment with others.
Repetitive Behaviors and Restricted Interests
Repetitive Movements:
- Hand-flapping, rocking, spinning, or other repetitive physical actions.
Insistence on Sameness:
- Strong preference for routines and resistance to change (e.g., specific routes to school).
Intense Focus on Specific Interests:
- Developing deep, often obsessive interests in particular topics or objects.
Sensitivity to Sensory Input:
- Overreacting or underreacting to sensory stimuli, such as lights, sounds, or textures.
Treatment options for autism in children focus on supporting development and addressing specific challenges. Here are some common approaches:
Behavioral Interventions:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Uses reinforcement techniques to teach new skills and reduce challenging behaviors.
- Natural Language Acquisition (NLA): Encourages language development through natural interactions.
Therapeutic Approaches:
- Speech Therapy: Helps improve communication skills, including both verbal and non-verbal communication.
- Occupational Therapy (OT): Focuses on developing daily living skills and sensory integration.
- Social Skills Training: Teaches children how to interact appropriately with peers and understand social cues.
Educational Support:
- Individualized Education Programs (IEPs): Tailored educational plans that address a child’s specific needs in a school setting.
- Special Education Services: Provides additional support in the classroom to help children succeed academically and socially.
Medication:
- While there is no medication to cure autism, some medications can help manage symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or hyperactivity.
Parent Training and Support:
- Programs that educate parents on strategies to support their child’s development and behavior, as well as support groups for shared experiences and advice.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies:
- Some families explore options like dietary changes, mindfulness, or sensory integration therapies, though it’s essential to discuss these with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) in children is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects their ability to focus, control impulses, and regulate their activity levels. It can manifest in various ways, often categorized into three main types: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and combined presentation.
Key Signs and Symptoms
Inattention:
- Difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play activities.
- Frequent careless mistakes in schoolwork or other activities.
- Trouble organizing tasks and activities.
- Often loses items necessary for tasks (e.g., school supplies, toys).
- Forgetfulness in daily routines.
Hyperactivity:
- Fidgeting or tapping hands or feet.
- Difficulty remaining seated in situations where it’s expected (like in class).
- Running or climbing in inappropriate situations.
- Talking excessively or interrupting others.
Impulsivity:
- Difficulty waiting for their turn in group activities.
- Blurting out answers before questions are completed.
- Interrupting or intruding on others’ conversations or games.
Treatment options for ADHD in children often involve a combination of behavioral therapies, educational support, and, when necessary, medication. Here’s a closer look at these options:
1. Behavioral Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps children develop coping strategies, improve organizational skills, and manage emotions.
- Parent Training: Educates parents on effective strategies for managing behavior and implementing consistent routines.
- Social Skills Training: Teaches children how to interact appropriately with peers and develop better social relationships.
2. Medication
- Stimulant Medications: These are the most commonly prescribed and include:
- Methylphenidate (e.g., Ritalin, Concerta)
- Amphetamines (e.g., Adderall, Vyvanse)
- Non-Stimulant Medications: These may be prescribed if stimulants are not effective or cause side effects. Options include:
- Atomoxetine (Strattera)
- Guanfacine (Intuniv)
3. Educational Support
- Individualized Education Programs (IEPs): Tailored plans that outline specific educational goals and accommodations to support learning.
- 504 Plans: Provide accommodations for children who do not qualify for an IEP but still need support in the classroom.
- Classroom Strategies: Techniques such as structured routines, clear instructions, and frequent breaks can help children stay focused.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Encouraging balanced nutrition can support overall health and potentially improve attention.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce symptoms of ADHD and improve mood.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep routine can improve focus and overall functioning.
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders that affect movement, muscle coordination, and posture. It is caused by abnormal brain development or damage to the developing brain, often occurring before, during, or shortly after birth. In children, CP manifests in various ways, affecting their ability to control muscles and movements.